What is the quantum internet? | University of Chicago News
The quantum internet is a network of quantum computers that will someday send, compute, and receive information encoded in quantum states.
The quantum internet will not replace the modern or “classical” internet; instead,
it will provide new functionalities such as quantum cryptography and quantum cloud computing.
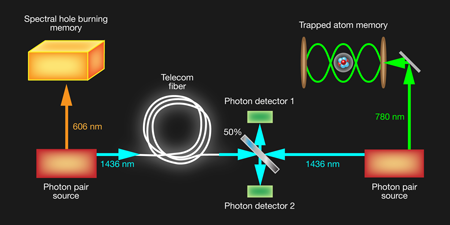
Quantum internet utilizes quantum bits (qubits) instead of classical binary bits. The fascinating property of qubits is that the mere act of observing them changes their state – making it impossible for hackers to intercept messages without detection. This isn’t theoretical physics; it’s happening now. Countries like China already have satellites in orbit sending quantum-encrypted messages.
Bernardo Huberman is a fellow and vice president of the Next-Gen Systems Team at CableLabs.
[1] He is also a consulting professor in the Department of Applied Physics and the Symbolic System Program at
Stanford University.
It involves the sharing of information at atomic and subatomic levels through quantum channels. Compared to classical computing, it can share information at infinitely higher rates and with vastly fewer limitations. It is also a great deal more secure than classical computing.
No comments:
Post a Comment