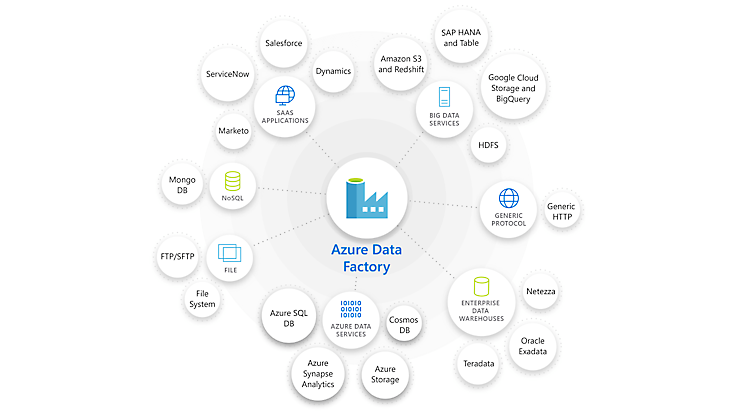
Azure RBAC documentation | Microsoft LearnAzure Role-Based Access Control (Azure RBAC) is a system that provides fine-grained access management of Azure resources. Using Azure RBAC, you can segregate duties within your team and grant only the amount of access to users that they need to perform their jobs.
A
security principal ("who") is an object that represents a user, group, service principal, or managed identity that is requesting access to Azure resources. You can assign a role to any of these security principals.

A
role definition ("
what") is a collection of permissions. It's typically just called a role. A role definition lists the actions that can be performed, such as read, write, and delete. Roles can be high-level, like owner, or specific, like virtual machine reader.
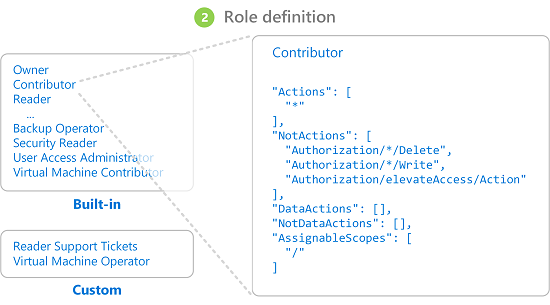
Azure includes several built-in roles that you can use.
If the built-in roles don't meet the specific needs of your organization,
you can create your own Azure custom roles.
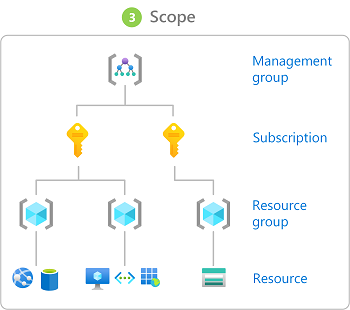
Scope ("
where") is the set of resources that the access applies to. When you assign a role, you can further limit the actions allowed by defining a scope. This is helpful if you want to make someone a
Website Contributor, but only for one resource group.
In Azure, you can specify a scope at four levels:
management group, subscription,
resource group, or resource. Scopes are structured in a parent-child relationship. You can assign roles at any of these levels of scope.
A role assignment is the process of attaching a role definition to a user, group, service principal, or managed identity at a particular scope for the purpose of granting access. Access is granted by creating a role assignment, and access is revoked by removing a role assignment.