Generating sortable Guids using NewId
pros-and-cons of using database-generated integer vs client-generated Guids, and introduce NewId as a way of mitigating some of the downsides of Guids.
phatboyg/NewId: A sequential id generator that works across nodes with no collisions @GitHub
.NET Guid.NewGuid()
NewId is designed to solve a specific problem. It's for when you want a unique ID, but you want them to generally be sortable, and semi-predictable.
example
be170000-f32d-18db-de59-08da26f2ad5a
be170000-f32d-18db-1816-08da26f2ad5b
be170000-f32d-18db-8694-08da26f2ad5b
be170000-f32d-18db-4dbd-08da26f2ad5b
be170000-f32d-18db-65b3-08da26f2ad5cbe170000-f32d-18db—this is apparently constant across all IDs.de59—this changes with every ID.08da26f2ad5a—this sometimes changes, and changes gradually.
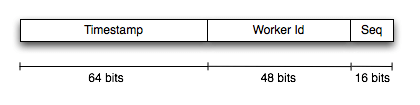
NewId uses 3 different sources to construct an ID
- A "worker/process ID". This is constant for a given machine (and can be configured to also include the process ID).
- A "timestamp". This provides the basic ordering of the ID
- A "sequence". An incrementing ID.
By combining all 3 together, you can get an ID that is (roughly) orderable, thanks to the timestamp component. By including the worker ID you can have workers independently generate IDS while avoiding collisions. And the use of the "sequence" means you can generate 216-1 IDs per millisecond, per worker:
Guids have caused nearly 99% fragmentation in the (SQL server database) index, whereas the NewIds have caused only a 5% fragmentation. crypto library.