Data are often stored in proprietary or custom formats.
Complex data are often inherently graphs (not chart).
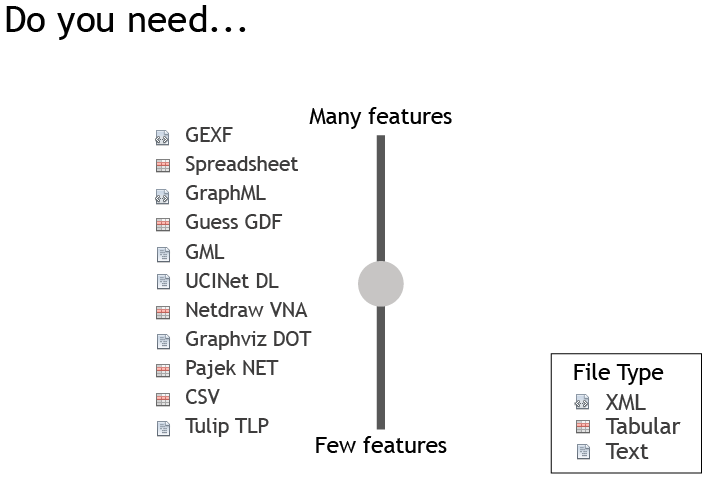
There are many serialization formats for representing graphs.
Domain-specific graph formats are simpler, while often limited to visualization.
General-purpose formats are often verbose not intuitive.
RDF (from semantic web) is most general, specific, and often quite verbose (XML)
while its N3 variant is very compact and simple.

DOT (graph description language) - Wikipedia
undirected
// The graph name and the semicolons are optional graph graphname { a -- b -- c; b -- d; }
directed
digraph graphname { a -> b -> c; b -> d; }
Supported Graph Formats
GraphML Format
Graphviz - Wikipedia
Graphviz Online
Viz.js
mdaines/viz.js: A hack to put Graphviz on the web.
Dagre: Graphs in JavaScript
magjac/d3-graphviz: Graphviz DOT rendering and animated transitions using D3
d3-graphviz Demo - bl.ocks.org
canviz: graphviz on a canvas
koops/canviz: Fork of Canviz by Ryan Schmidt
Running Graphviz in Javascript
JSON Graph Format Specification Website
jsongraph/json-graph-specification: A proposal for representing graph structure (nodes / edges) in JSON.
{
"graph": {
"directed": false,
"type": "graph type",
"label": "graph label",
"metadata": {
"user-defined": "values"
},
"nodes": [
{
"id": "0",
"type": "node type",
"label": "node label(0)",
"metadata": {
"user-defined": "values"
}
},
{
"id": "1",
"type": "node type",
"label": "node label(1)",
"metadata": {
"user-defined": "values"
}
}
],
"edges": [
{
"source": "0",
"relation": "edge relationship",
"target": "1",
"directed": false,
"label": "edge label",
"metadata": {
"user-defined": "values"
}
}
]
}
}
alternatives
bruth/json-graph-spec: JSON specification for representing a graph structure
Resource Description Framework - Wikipedia
(RDF N3) Notation3 - Wikipedia
Tutorial 1: Introducing Graph Data
RDF Triple Stores vs. Labeled Property Graphs: What's the Difference? @ Neo4j
No comments:
Post a Comment